what are ketone body Ketone bodies three acetoacetate keto ketosis body beta hydroxybutyrate acetone formation middle state definition biology above left glucose
Ketone bodies are organic compounds that are produced by the liver when the body undergoes a metabolic state known as ketosis. This occurs when there is a lack of dietary carbohydrates, forcing the body to use stored fat as the primary source of energy. The process of breaking down fat to produce ketone bodies is known as ketogenesis.
Ketone Bodies
Ketone bodies are important for individuals following a ketogenic diet as well as those with certain medical conditions such as diabetes. The three main ketone bodies are acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate. These compounds provide an alternative fuel source for the brain and other organs when glucose levels are low.
 Acetone is the simplest ketone body and is responsible for the keto breath sometimes experienced by individuals in ketosis. Acetoacetate can be converted into beta-hydroxybutyrate, the primary ketone body used for energy in the body. Beta-hydroxybutyrate can easily cross the blood-brain barrier and provide fuel for the brain when glucose availability is limited.
Acetone is the simplest ketone body and is responsible for the keto breath sometimes experienced by individuals in ketosis. Acetoacetate can be converted into beta-hydroxybutyrate, the primary ketone body used for energy in the body. Beta-hydroxybutyrate can easily cross the blood-brain barrier and provide fuel for the brain when glucose availability is limited.
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential benefits for weight loss and overall health. The diet aims to induce a state of ketosis, where the body enters a metabolic state that efficiently burns fat for energy.
 By limiting carbohydrate intake to a minimum, the ketogenic diet forces the body to switch from using glucose as its primary fuel source to using ketone bodies. This shift triggers numerous physiological changes that may have a positive impact on weight loss, blood sugar control, and overall metabolic health.
By limiting carbohydrate intake to a minimum, the ketogenic diet forces the body to switch from using glucose as its primary fuel source to using ketone bodies. This shift triggers numerous physiological changes that may have a positive impact on weight loss, blood sugar control, and overall metabolic health.
It is important to note that the ketogenic diet should be followed under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with underlying medical conditions or those taking certain medications.
In conclusion, ketone bodies play a crucial role in the body’s ability to adapt to a state of ketosis, particularly when following a ketogenic diet. Understanding the science behind ketone bodies can help individuals make informed decisions about their dietary choices and potential health benefits.
If you are looking for Ketone Bodies: Definition, Formation and Function | Biology Dictionary you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Images about Ketone Bodies: Definition, Formation and Function | Biology Dictionary like Ketone Bodies: Definition, Formation and Function | Biology Dictionary, Figure 1 from Ketone body metabolism and cardiovascular disease and also USMLE Notes - Ketone bodies are produced in the liver and can be…. Read more:
Ketone Bodies: Definition, Formation And Function | Biology Dictionary
 biologydictionary.netketone bodies three acetoacetate keto ketosis body beta hydroxybutyrate acetone formation middle state definition biology above left glucose
biologydictionary.netketone bodies three acetoacetate keto ketosis body beta hydroxybutyrate acetone formation middle state definition biology above left glucose
What Is The Ketogenic Diet?
 www.dirt-to-dinner.comketones ketone bodies acetone ketogenic bhb acetoacetate hydroxybutyrate urine metabolism blood hydroxybutyric salts ketosis ketoacidosis perfectketo fatty state tissues nutritional
www.dirt-to-dinner.comketones ketone bodies acetone ketogenic bhb acetoacetate hydroxybutyrate urine metabolism blood hydroxybutyric salts ketosis ketoacidosis perfectketo fatty state tissues nutritional
Ketone Bodies
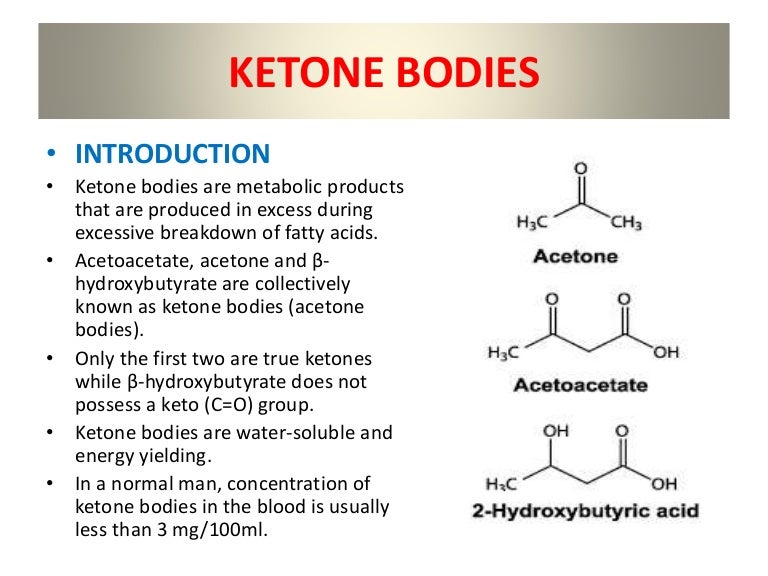
 www.slideshare.netketone bodies liver made fatty body regulated disease slideshare produced breakdown fats metabolic introduction excess fuels
www.slideshare.netketone bodies liver made fatty body regulated disease slideshare produced breakdown fats metabolic introduction excess fuels
USMLE Notes - Ketone Bodies Are Produced In The Liver And Can Be…
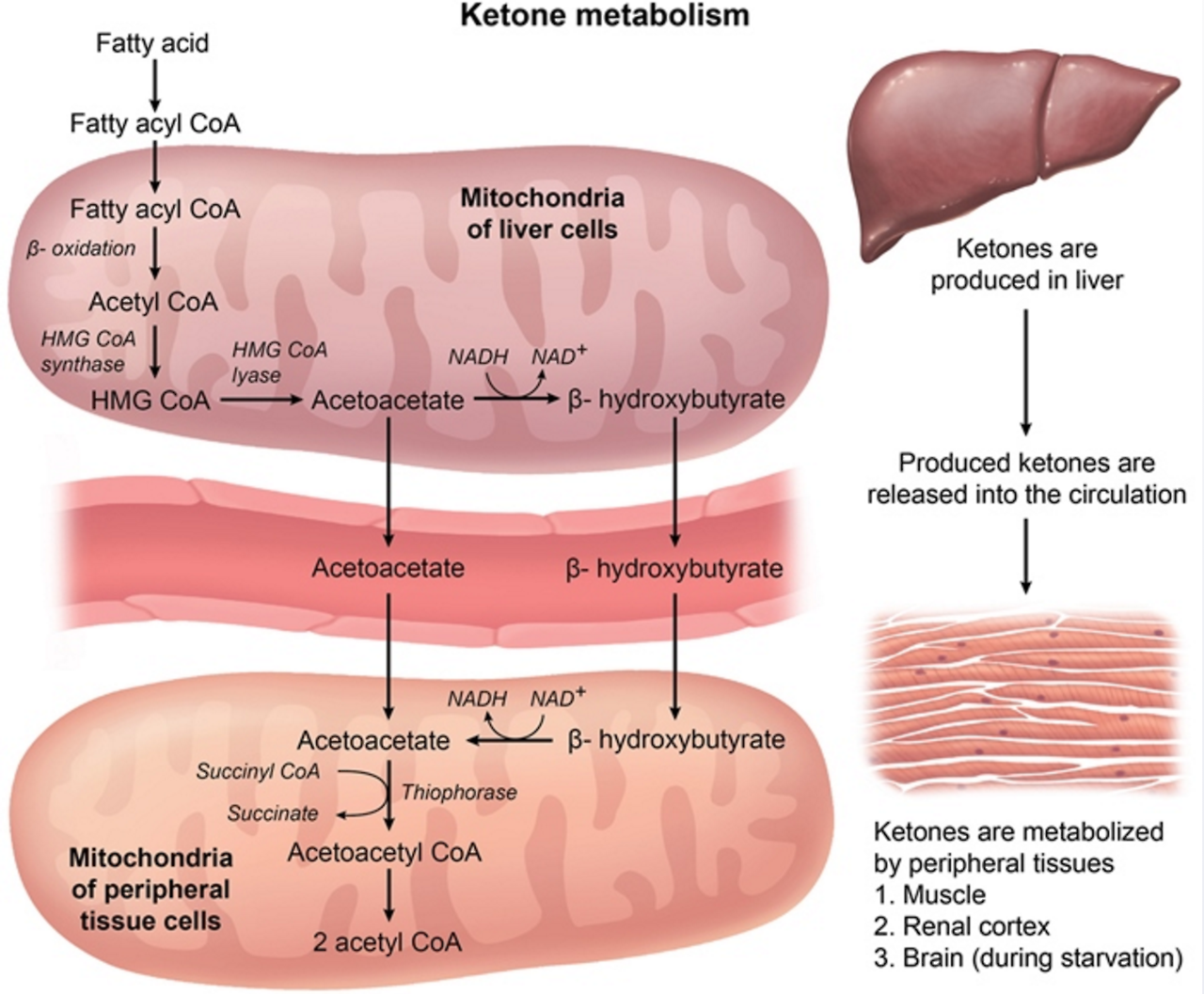 usmle-notes.tumblr.comketone liver usmle mitochondrial peripheral ketones mitochondria tissues
usmle-notes.tumblr.comketone liver usmle mitochondrial peripheral ketones mitochondria tissues
Figure 1 From Ketone Body Metabolism And Cardiovascular Disease
 www.semanticscholar.orgketone metabolism body disease
www.semanticscholar.orgketone metabolism body disease
Ketone metabolism body disease. Ketone bodies. Ketone liver usmle mitochondrial peripheral ketones mitochondria tissues